Scarring of your skin is a natural part of the healing process after injury has occurred. It can be caused by a number of sources, most typically via injury, but also from conditions such as acne. Scars go through numerous changes as they heal, but they are permanent in nature. The nature and size of the injury to your skin, as well as your age will determine the characteristics of scarring that occurs, and how your skin reacts. However, scar tissue is not identical to the skin it replaces due to the fact that it does not regenerate like normal skin. The tough fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin and forms a scar, is made up of cells called fibroblasts which ensure that the wound heals completely. Severe scarring is typically remedied by surgery, skin grafts or laser resurfacing treatments.
Under Your Skin
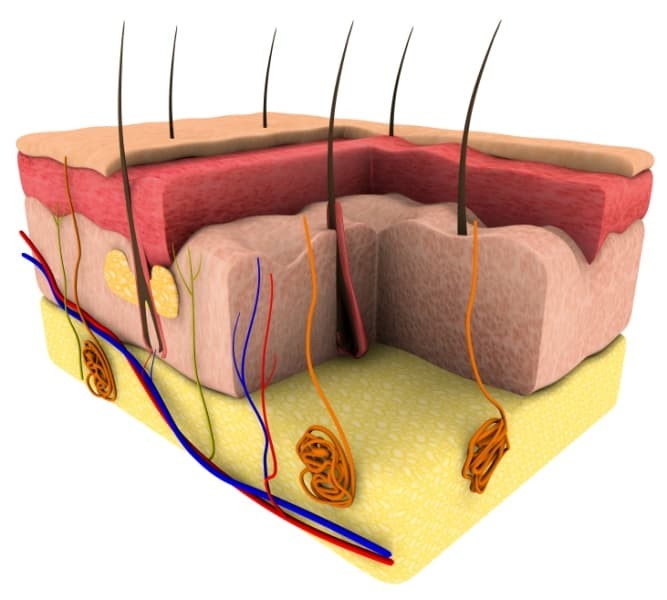
Skin is an extremely versatile organ, which covers your entire body. Skin is made up of three layers that consist of:
- a thin outer layer or epidermis contains dead skin cells that are continually shed, as well as cells that produce melanin, which gives your skin its colour.
- a middle layer or dermis contains elastin (which gives skin its elasticity), and collagen for strength. The nerves in the dermis provide us with our senses such as touch and spatial awareness. The dermis has blood vessels which supply the tissues with nutrients and oxygen and also help the body manage temperature. Other components include lymph vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and the sebaceous glands, which produce oil.
- an inner layer or hypodermis mostly made up of fat. It lies between the dermis and muscles or bones and contains blood vessels that expand and contract to help keep your body at a constant temperature. This layer also protects your vital inner organs.
The primary functions of skin are varied, but include:
- Protection - a barrier to infection of our internal organs, whilst also secreting wastes in the form of sweat
- Regulation - of temperature via blood vessels that contract or dilate near the skins surface
- Sensory function - nerves endings in the dermis react to stimuli such as heat, cold, pressure or pain allowing us to react accordingly
Natural Therapies for Skin Scars
Most people with minor or superficial scarring require less invasive and abrasive treatment methods. The regular application of natural topical treatments can relieve and improve the appearance of scarring. It is also highly effective in helping to maintain the elasticity of scar tissue on joints and other high-mobility areas. These include:
- Vitamin E, which is a powerful antioxidant that increases the moisture content of the epidermis, whilst making the skin more supple
- Lavender oil is well known for its skin conditioning properties
- Vitamin A (Retinyl) helps improve the skin's elasticity, texture and tone
- Rosemary oil helps to invigorate and condition the skin
- Chamomile oil is renowned for its calming and soothing effect, especially for sensitive skin
- Calendula oils or marigold, is a natural antioxidant that has the ability to clarify and condition the skin
- Aloe vera gel is an anti-inflammatory agent
- Olive oil helps to regenerate skin
- Honey is effective in aiding wounds to heal
Looking After Your Skin
You can also follow these simple lifestyle guidelines for a healthier skin:
- Drink plenty of water. This will help keep your skin hydrated and lend your body a helping hand in clearing up any acne scarring.
- Prevention is also the best cure! Wear sun block, UV protection sun glasses and a hat when you are outdoors.
- A balanced diet should include daily intakes of fresh fruit and vegetables which will help your skin retain its condition.
Consult your local beauty therapist or dermatologist if you have concerns about your skin and any scarring you may have.
Originally published on Jun 18, 2009