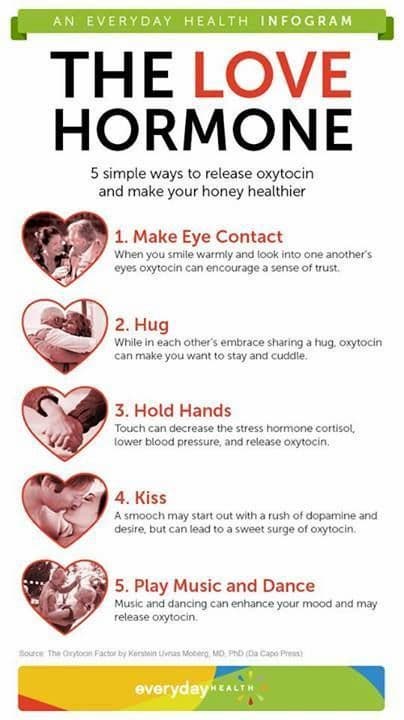
You know that feeling you get when you hug or kiss the love of your life? It’s all down to oxytocin, which is also known as the cuddle hormone—a powerful hormone that connects you and your partner and acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain, controlling reproduction. Here, we put oxytocin under the microscope.
Oxytocin 101
Made in the hypothalamus, oxytocin enters the bloodstream via the posterior pituitary gland. This happens when the cells are stimulated. Oxytocin influences the breasts and uterus, as well as other organs. During childbirth, oxytocin causes the uterine muscles to contract. At the same time, prostaglandins are produced to aid childbirth. When breastfeeding, oxytocin helps the milk move into the breast, ready for release. And in men, oxytocin is an important player in testosterone production and sperm movement.
The Love Hormone
Since it works as a chemical messenger, oxytocin increases arousal and connects partners during intimacy. That’s why it’s commonly called the cuddle chemical or love hormone. It bonds us with our partner while increasing trust and passion. German researchers believe that oxytocin could stop us straying from our partner. In what could be described as the most colourful social study, an ‘attractive researcher’ was asked to move closer towards men who had received an oxytocin or placebo nasal spray. Men who were in monogamous relationships favoured more distance between them and the researcher, suggesting oxytocin ties us to our partners.
While oxytocin is commonly associated with romantic attachment between couples, it generally plays an important role in increasing interaction between humans and strengthening other types of social relationships, including those shared between mother and child, friends, teachers and students, and co-workers.
How the Release of Oxytocin Benefits Health
Interestingly, researchers believe there could be an association between autism and oxytocin and that increasing oxytocin in people with autism could help with treatment. Oxytocin can be used to improve the social skills of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), such as improving their emotional recognition, speech and social interaction. It has even been suggested that oxytocin receptors, because of their antidepressant-like effects without the side effects of the pill, could help treat a wide range of health issues, including the following:
- Anxiety disorders
- Depression
- Stress-related disorders
- Erectile dysfunction
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Obesity
- Addiction
- Asthma
- Alzheimer's disease
Oxytocin can improve your health physically and mentally in many ways. This peptide hormone has anti-stress effects and anti-inflammatory properties that help your body heal faster after injury or illness. Oxytocin may also increase immune function by increasing antibody production and decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines. Other benefits include:
- Reduces cravings (e.g. alcohol)
- Improves memory formation (particularly emotional memories)
- Helps manage the body's stress response
- Enhances communication skills by increasing eye contact, empathy and reducing stress levels when talking with other people
- Improves your mood by increasing trust between you and other people
- Reduces symptoms of psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, PTSD and social phobia
- Assists in the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage, which results from uterine rupture
- Increases uterine activity
- Decreases blood pressure
- Controls production of stress hormones
Oxytocin: Too Much or Too Little?
Science has been slow to study whether the positive effects of oxytocin can shift to negative if you have too much or too little oxytocin production, though it has been suggested that small amounts of oxytocin may make it difficult for a woman to secrete milk supply during childbirth. On the other end of the spectrum, excessive levels of oxytocin could cause a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia, which can cause urination difficulties in men. If you have concerns about your oxytocin levels, consult your healthcare provider.
Prompting the Rise of Oxytocin Levels
The levels of oxytocin quickly degrade in the body. Upon the release of oxytocin, along with other pituitary hormones, it only stays in the body for about one minute, so measuring it directly is impossible. Researchers use indirect measures of oxytocin release, such as salivary oxytocin.
One study asked participants to relax for five minutes while listening to soothing music or watching a romantic film, which was used as an indicator that oxytocin release had occurred. Researchers have found a positive correlation between watching a romantic film and the rise of oxytocin levels.
Source: infographicnow.com
Other ways to trigger oxytocin release are as follows:
Drinking whole milk
You may have heard that oxytocin is released by breastfeeding mothers when they nurse their babies. What you may not know, however, is that oxytocin can also be released via oxytocin receptors in your gut after drinking whole milk or eating chocolate. Whole milk contains oxytocin-enhancing compounds like whey protein, and the amino acid cysteine (which activates oxytocin release). Plain yoghurt with active bacterial cultures will also work because of its high concentration of cysteine.
Eating small meals frequently
Oxytocin levels are also increased by eating more often - small, frequent meals instead of three large ones - so it's important to have five or six daily meals. That's great news for oxytocin! To boost your oxytocin levels, eat more avocados, spinach, fatty fish, eggs, cottage cheese, ricotta cheese and nuts.
Including helpful herbs in your diet
Herbs such as maca and chasteberry (vitex) may be able to increase oxytocin levels naturally by activating the oxytocin receptors in the body. Oxytocin levels can also be increased by ingesting ginseng. A randomised trial found that oxytocin levels in participants' blood were elevated after being given ginseng and oxytocin nasal spray. In Japan, China and other Asian countries, Panax ginseng is commonly used as a tonic herb to restore hormonal balance and strengthen the immune system. One of the active ingredients in ginseng is believed to activate oxytocin receptors without entering into cells. Therefore, this ingredient may enhance oxytocin naturally while not promoting a high level of toxicity for humans or animals.
Getting a massage
Massage therapy activates oxytocin receptor cells, according to clinical trials conducted to determine ways to boost the level of oxytocin after it has dropped. This, in turn, increases oxytocin secretion.
Increasing sexual activity
Given the role of oxytocin in human reproduction and other health benefits, it is not surprising that oxytocin levels rise following sexual arousal or orgasm. Oxytocin also contributes to male sexuality by increasing libido and penile erection.
Eating chocolates
Evidence from human studies suggests that eating chocolate increased the production of endogenous oxytocin. This decadent treat has been shown to stimulate brain regions involved in pleasure and reward.
Increasing social interaction
Oxytocin levels are raised not only by amorous gestures, but also by other forms of physical contact, such as making eye contact, smiling, talking, singing and eating together. If there's no way you can be physically close to friends or family members, use your social media tools to foster positive relationships and trigger the expected actions of oxytocin, such as reduced stress reactions and improved social functioning.
Whether it is to reduce your anxiety, promote wound healing, improve mental health, reduce depression, improve sleep or even help you recover from an injury, maintaining the right amounts of oxytocin in your body can do it all. And the best part is, oxytocin doesn't have any adverse effects like prescription drugs.
Originally published on Sep 09, 2013