Has anyone ever told you that you are more "right-brained" or more "left-brained"? Do you wonder what it all means and if there's even any difference? You would be surprised! Read this article to find out how the two distinct halves of the brain affect your everyday life.
The Two Halves of the Brain
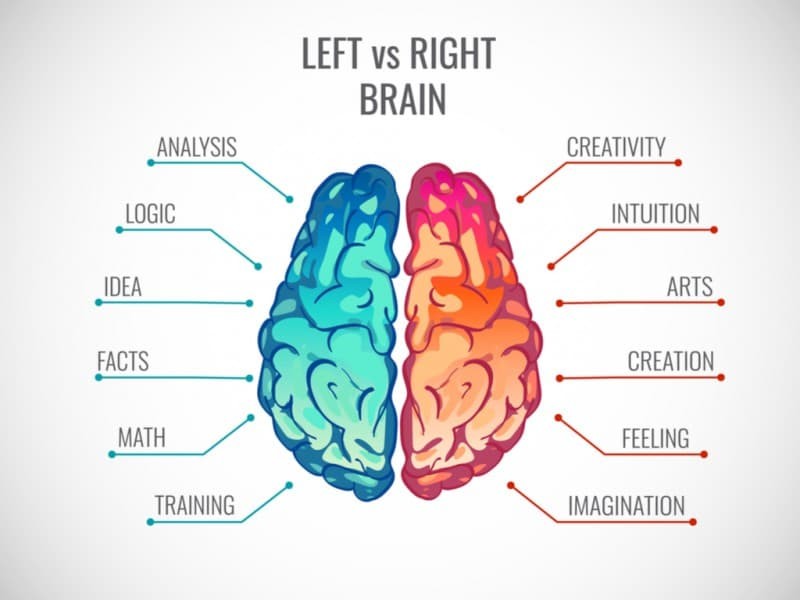
The human brain is the body's control centre that processes our bodily sensations, emotions and perceptions. It is also believed to be responsible for moulding our personalities, talents and skills. Every single person has a right brain and a left brain. The two different sides of the brain control two different types of thinking. The right brain is the "creative" side while the left brain is the "logical" side.
Research reveals that most people prefer only one style of thinking over the other. Some people are naturally more creative or right-brained, while others are more logical, making them left-brained. Ironically, the right side of the brain controls the muscles on the left side of the body, while the left hemisphere controls the motor skills of the right side of the body. That means, left-handed people have a stronger right hemisphere, while right-handed people have a more dominant left brain.
There is a fold that goes from the front to the back of the brain, essentially dividing it into two different parts. The "corpus callosum" is a thick bundle of nerves at the base of the brain connecting the two different parts. Additionally, it wires the right side of the body to the left side of the brain and vice versa. This crossover is applicable to all areas of the body, including the eyes, which process a majority of their sensory data on the opposites of the brain.
Research has also revealed that most children are ranked as being highly creative (right-brained) before they enter school. By the time they reach the age of 7, only ten percent of them are ranked as highly creative. This is because the education system has placed more value on left brain skills, which include mathematics, logic and language. By the time they reach adulthood, only two percent of the population is ranked as being highly creative.
The Impact of Brain Lateralization on Cognitive Functions
Numerous studies have supported the concept of brain lateralization and its influence on cognitive functions. Brain imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), have revealed distinct patterns of brain activity during various tasks. For example, when engaging in language-related activities, increased neural activity is observed in the left hemisphere. Similarly, creative endeavors activate the right hemisphere to a greater extent.
It's important to note that while the left and right brain hemispheres have distinct functions, they work together in harmony. They are interconnected by a bundle of nerve fibres called the corpus callosum, which facilitates communication and coordination between the two hemispheres. This interconnectedness allows for a more integrated and holistic cognitive experience.
Brain lateralization plays a crucial role in shaping our cognitive functions. While the left and right brain hemispheres have their unique strengths, they work in collaboration to create a comprehensive cognitive experience. Understanding and harnessing the power of both hemispheres can lead to enhanced problem-solving abilities, creativity, and a more balanced approach to thinking.
The Processing Activity of Both Brain Hemispheres

The right side of the brain looks at the whole first before it breaks things down into parts. It is also random. A right-brained person is more likely to move from one task to the other – completing the same amount of work done by a left-brained person but without paying attention to priorities. The right side likes everything to be concrete. It likes to be able to see, feel or touch the real object. It also likes context. Right-brained people are said to know what they mean but often have trouble in verbally expressing them.
The left brain, in contrast, processes information in a linear manner and from a part to a whole. It takes every piece of information, lines them up and then arranges them into a logical order before forming conclusions. It also processes in sequence, so tasks are finished in order. Left-brained people easily learn things in a sequence as they apply linear thinking. The left side of the brain processes symbols including letters, words and mathematical notations. Left-brained people are known to easily cope with mathematical and linguistic tasks and they have excellent verbal skills.
The Functions of the Right Brain
The right hemisphere of the brain is perceived as the "creative" side. Left-handed people are right hemisphere dominant and excel in music and the arts, with the majority of them taking on jobs where the imagination, emotions and creativity matter more than math skills and language processing. The right brain is responsible for some cognitive functions, including processing of patterns, colors and shapes as well as emotions, dreams and unspoken language. It is holistic, subjective and synthesising, as well as bearing the following characteristics:
- Uses feelings
- Big picture oriented
- Imaginative
- Uses symbols and images
- Present and future thinking
- Philosophy and religion
- Freethinking
- Intuitive
- Appreciative
- Spatial perception
- Knows object function
- Fantasy-based
- Presents possibilities
- Impetuous
- Risk taker
Also, some of the abilities that are associated with the right brain include:
- Facial recognition
- Expressive
- Musically inclined
- Reading emotions
- Drawn to colors
- Imaginative
- Intuitive
The Functions of the Left Brain
The left side of the brain is perceived as the "logical" side. It is the seat of language - verbal and sign language - and responsible for the learning style of a person. Right-handed people are organised, objective and flourish in jobs that require computations and language comprehension. The left hemisphere of the brain has the following characteristics:
- Uses logic
- Detail-oriented
- Relies on facts
- Controls words and language
- Present and past thinking
- Inclined to math and science
- Can comprehend
- Has the ability of knowing
- Acknowledges
- Follows an order/pattern
- Perception
- Knows object name
- Reality based
- Forms strategies
- Practical
- Cautious
Also, some of the abilities that are associated with the left brain include:
- Control of language
- Logical reasoning
- Critical thinking
- Numbers
Harnessing the Power of a Whole-Brain Approach
The human brain is a remarkable organ with the capacity for incredible cognitive feats. By embracing a whole-brain approach, we can harness the power of both the left and right hemispheres, leading to enhanced thinking, problem-solving and creativity.
A whole-brain approach recognises that optimal cognitive functioning arises from the integration of logical and analytical thinking with creative and intuitive abilities. This balanced approach allows for a comprehensive and flexible cognitive experience.
To cultivate a whole-brain mindset, it's essential to engage in activities that stimulate and challenge both hemispheres.
Here are a few practical tips and techniques:
Cross-disciplinary Learning
Explore diverse subjects and disciplines that require different cognitive skills. By venturing beyond your comfort zone, you can exercise both analytical and creative thinking.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Practise mindfulness and meditation to enhance awareness and focus. These practices promote a state of heightened attention and can help integrate brain functions for improved cognitive performance.
Brainstorming and Idea Generation
Engage in brainstorming sessions or creative exercises that encourage free-flowing ideation. Embrace unconventional and imaginative approaches to problem-solving.
Physical Exercise
Regular physical exercise improves blood flow to the brain and enhances overall cognitive function. Activities such as dancing, playing sports or practising yoga can engage both hemispheres, fostering brain integration.
Music and Art Appreciation
Immerse yourself in the world of music and art. Listening to diverse genres of music and exploring various forms of artistic expression stimulates both logical analysis and creative interpretation.
What Research Says About Brain Functions and Dominance
Several studies have debunked the old brain theory and straightened out information regarding hemispheric differences. Recent research has shown that the human brain has a symmetrical structure for a reason; everyone uses both brain regions equally unless one side has been damaged due to a brain injury.
After studying the brains of 1,000 people using an MRI, a 2013 scientific article published by PLOS One concluded that there's no such thing as a dominant brain because a person uses both sides of their brain, depending on the task that needs to be completed.
How the left hemisphere of the brain emerged as more dominant than the right stemmed from the split-brain study of neuropsychologist Roger W. Sperry in the 1960s, which won him the Nobel Prize. According to PLOS Biology, the study involved patients who had undergone split-brain surgery, wherein the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres was removed to address a type of severe epilepsy. After testing each hemisphere, the language centres were revealed in the left and emotional and nonverbal functions in the right.
However, Sperry's findings were exaggerated by many ill-founded publications that immortalised the popular belief that the right hemisphere is responsible for creativity in the world of art, business and education.
The Mysteries of the Left and Right Brain: Key Findings from Clinical Trials
1. "Brain Lateralization and Language Processing" - University of Melbourne
A clinical trial conducted at the University of Melbourne examined the relationship between brain lateralization and language processing. The study involved neuroimaging techniques to observe brain activity during language-related tasks. Results indicated a strong left hemisphere dominance for language functions, highlighting the role of the left brain in linguistic processes. This study provided evidence supporting the concept of lateralization for language processing in the Australian context.
2. "Creativity and the Right Hemisphere" - Queensland University of Technology
Researchers at the Queensland University of Technology explored the connection between creativity and the right hemisphere of the brain. The study involved a series of experiments to assess creative thinking abilities and brain activity patterns. Findings indicated a positive correlation between heightened creative thinking and increased right hemisphere activation. This study reinforced the notion that the right brain plays a significant role in creative processes, offering valuable insights into fostering creativity among individuals.
3. "Brain Integration and Cognitive Flexibility" - Monash University:
A study conducted at Monash University focused on the concept of brain integration and its impact on cognitive flexibility. Researchers investigated how the interconnectedness between the left and right hemispheres influenced problem-solving abilities and adaptability. The study involved cognitive assessments and brain imaging techniques. The results suggested that individuals with a higher degree of brain integration demonstrated enhanced cognitive flexibility. This study highlighted the importance of nurturing whole-brain thinking for improved problem-solving skills.
4. "Neuroplasticity and Brain Training" - University of Sydney
Researchers at the University of Sydney conducted a clinical trial exploring the role of neuroplasticity in brain training programs. The study involved participants engaging in cognitive exercises designed to stimulate neuroplasticity and promote brain integration. The findings revealed that targeted brain training activities led to significant improvements in cognitive abilities, memory and attention. This study emphasised the potential for individuals to actively reshape their brain functions through intentional practices.
Achieving a Healthy Brain

While there's no evidence to prove that people who are right-handed have a better cognitive function and those who are left-handed are more creative, everybody can improve their brain functions if they have the will to do it.
Researchers found that specific thinking exercises can improve the brain cells in both hemispheres and promote a healthy brain. If you want to learn holistic thinking and become more creative, dabbling in colouring books, practising mindfulness and engaging in physical exercises will improve the performance of your cerebral cortex. On the other hand, solving puzzles, writing, solving math problems and reading a lot will enhance logical thinking and speech production.
Art therapy, brain gym and educational kinesiology can also boost brain health as these modalities promote the fun and advantages of lifelong learning.
Originally published on Aug 31, 2008









