
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat that can increase the risk of stroke. It affects people of all ages, but is more common in older people. In Australia, it is estimated that atrial fibrillation affects at least 340,000 people, and the rate of AF-related mortality continues to increase as our population ages. This heart condition can lead to heart failure and other medical conditions if it's not treated immediately, so proper management of patients with atrial fibrillation is paramount.
Read on to find out what causes an irregular heart rhythm, which is the most common symptom of atrial fibrillation, and what treatment methods can help improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
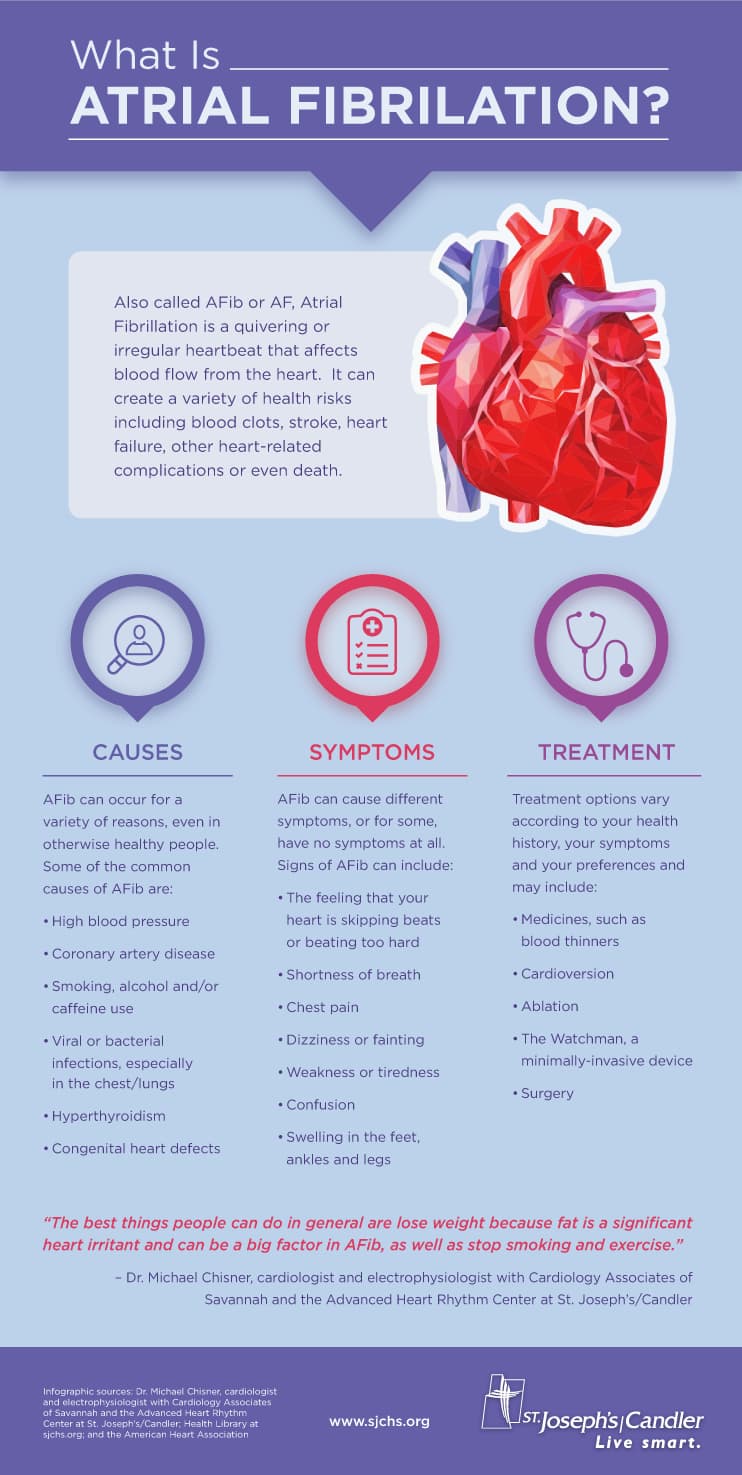
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation refers to an abnormal heart rhythm resulting from the heart's upper chambers beating out of sync with its lower chambers. A rapid heart rhythm is the hallmark of this condition, which can lead to blood clots in the heart or heart failure.
AF episodes vary from patient to patient. Some of them may manifest all of the signs associated with the disease, while others may not show any obvious atrial fibrillation symptoms. It's important to take steps to prevent atrial fibrillation, especially if you're at risk for the condition.
What are the Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is one of several types of arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) that can cause a variety of symptoms depending on the type and severity of the condition. The following are the most common warning signs:
- Heart palpitations
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Fatigue
- Cold sweats
In paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, these symptoms may come and go, and the abnormal heart rhythm in patients with this type of AF can last for as little as a few minutes or as long as a few hours. In persistent atrial fibrillation, the normal heartbeat does not return, and electrical cardioversion or heart rhythm medicines are required to restore normal heart rhythms. The hearts of people with long-term persistent AF experience an irregular rhythm for more than a year, whereas those with permanent AF will find it difficult, if not impossible, to restore their regular heart rhythm without antiarrhythmic drugs.
Source: St. Joseph's/Candler
What are the Risk Factors for Atrial Fibrillation?
There are a number of factors that can contribute to atrial fibrillation, including high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, structural heart disease, diabetes, sleep apnea, problems with heart valves, and a previous heart surgery.
Age and family history are also risk factors for atrial fibrillation. In some cases, atrial fibrillation may be caused by an underlying medical condition.
A number of lifestyle factors can also increase the risk of atrial fibrillation, including:
Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes can damage the heart chambers and contribute to atrial fibrillation.
Obesity
Being overweight or obese increases your risk of atrial fibrillation. Obesity is a major risk factor for atrial fibrillation, as it increases the likelihood of high blood pressure, diabetes and sleep apnea - all of which are associated with atrial fibrillation. Furthermore, obese individuals have an increased risk of stroke or heart disease.
Stress
Stress can trigger atrial fibrillation episodes. When you're stressed, your body releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones prepare your body for "fight or flight" by increasing your heart rate and blood pressure. Over time, this can put a strain on your heart and lead to atrial fibrillation.
Excessive alcohol consumption
Drinking alcohol excessively can damage the heart and lead to atrial fibrillation. Otherwise, you risk increasing your heart rate and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) levels. ANP is a hormone that helps to get rid of excess fluid from the body. When the levels of ANP are high, it can lead to atrial fibrillation.
Caffeine
Caffeine can trigger atrial fibrillation episodes. If you have atrial fibrillation, drinking too much coffee or tea, or eating chocolate can make your condition worse as it increases the heart rate and forces the heart muscle to exert more pressure, making the heart more prone to arrhythmias.
Illegal drugs
The use of illegal drugs is a common cause of atrial fibrillation. Drug abuse can damage the heart muscle and lead to atrial fibrillation. Cocaine, amphetamines, and other stimulants are the most common drugs that cause atrial fibrillation. These illegal drugs increase the heart rate and put strain on the heart muscle.
What are the Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation?
There are a number of treatment options available for atrial fibrillation, and the best option for each individual will depend on their specific situation. Some common treatments include:
- Medications to control the heart rate, calcium channel blockers, and anti - coagulants for patients who have a greater risk for stroke
- Electrical cardioversion to shock the heart back into a normal rhythm
- Heart surgery to repair underlying heart conditions; catheter ablation and the maze procedure are common surgical procedures for atrial fibrillation
Practising a heart-healthy lifestyle, such as quitting smoking or managing stress levels, may also be recommended. It is important to work with a health specialist to determine the best course of treatment.
How is Atrial Fibrillation Diagnosed?
Having your heart checked by a cardiologist should not only be done when you are at risk of heart failure, coronary heart disease or cardiovascular disease, among other conditions related to the major blood vessel that transports oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the various organ systems in the body. It will assist you in maintaining your heart's normal rhythm while ensuring the heart muscle works perfectly well during atrial contraction.
While chest discomfort and heart palpitations are clear indicators of atrial fibrillation, they may not always manifest. Sometimes this condition silently creeps up and makes its presence felt through a sudden heart attack, which we want to avoid. Even if you don't have heart palpitations or chest pain, it's best to consult your healthcare provider if you suffer high blood pressure or are at risk of heart disease.
Some of the diagnostic tests that can determine whether or not you have atrial fibrillation include:
- Blood tests to rule out other health conditions, such as hyperthyroidism, a thyroid disease characterised by an overactive thyroid
- Chest X-ray will show if you have a regular heartbeat and if your lungs are functioning properly
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) measures the electrical activity of the heart and can determine if you have an abnormal rhythm if extra heartbeats are detected
- Exercising testing is often used to screen for myocardial infarction or ischemic heart disease, and it can help determine if you have atrial fibrillation as it measures ventricular rates or contractions.
How Can Atrial Fibrillation be Prevented?
Because each of us has only one heart, it is extremely important to keep your heart healthy as this will lead to a better quality of life. Maintain a healthy weight and avoid cardiovascular disease by engaging in physical activity and eating heart-healthy foods. Aside from weight loss, a heart rate control strategy is essential, especially for patients with heart failure.
If you have atrial fibrillation, it's important to work with your doctor to manage your condition and prevent complications.









